BodyLogin Dataset: Multiview (old copy)
| Motivation | Description | Experimental Setup | Acquisition Scenarios | Downloads |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data Labels and Definitions | Citations | Acknowledgements | F.A.Q. | Contact |
Motivation
The problems of gesture recognition and gesture-based authentication are similar in the sense that they both involve users performing gestures. However, in the former problem the goal is to recognize the gesture regardless of the user, whereas in the latter problem the goal is to recognize the user regardless of the gesture. Although it might seem that a given dataset of gestures can be used interchangeably for studying both problems, e.g., analyzing user authentication performance using a gesture recognition dataset, this is not the case. Datasets for gesture recognition are typically gesture-centric meaning that they have high number of gestures-per-user (many gestures to classify, few users performing them) whereas studying authentication requires the opposite, namely a user-centric dataset which has a high number of users-per-gesture.
The gesture-dataset that is available through this website has 40 users performing each gesture.
The gestures in this dataset are acquired under a variety of real-world recording conditions that are described in the sections below.
Description
The BodyLogin Dataset: Multiview (BLD-M) contains 2 gesture types performed by 40 different college-affiliated users (27 men and 13 women of ages that are primarily in the range 18-33 years). Each subject was asked to perform 2 unique short gestures, each approximately 3 seconds long, each with 20 samples. Both gestures involve motion in the upper and lower body.
- S gesture: drawing an “S” shape with both hands. Although simplistic, this gesture is shared by all the users (harder for authentication).

- User-defined gesture: the user chooses his/her own gesture with no instruction. Although potentially complex, this gesture is unique for most users (easier for authentication).

Experimental Setup
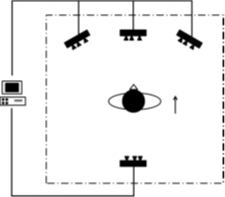
Each user gesture was captured using four Kinect cameras (version 1) for Windows. Three Kinects were placed facing the user and one Kinect was directly behind as shown in the figure to the right. Of the forward-facing Kinects, one was placed directly in the front (center) and two were offset by about 35 degrees to each side of the center. All devices were set up approximately 2 meters away from the user. Users were primarily facing the center camera for the duration of the performed gesture. All the Kinects were connected to a single PC to assure time synchronization. Captured frames were synced to the frame-rate of the center Kinect. Each Kinect camera captured a 640×480 depth image and skeletal joint coordinates at 30 fps. All data was captured using the official Microsoft Kinect SDK.
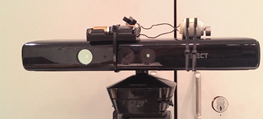
The simultaneous use of multiple Kinect cameras introduces structured light interference, which reduces the quality of the estimated depth maps. In order to reduce this interference, we applied an approach similar to the one developed by Butler et al. [link]; we attached Amico DC motors with a different number of revolutions per minute (RPM) to each camera as shown in the image to the left.
Acquisition Scenarios
Four different types of gesture acquisition scenarios were enacted to capture different types of real-world degradations: no degradations, personal effects, user memory, and gesture reproducibility.
- Personal effects: In the case of personal effects, users either wore or carried something when performing a gesture. Half of the users were told to wear heavier clothing, and the other half were told to carry some type of a bag.

Users wore a variety of heavier clothing: sweatshirts, windbreakers, and jackets.

They carried backpacks (either on a single shoulder or both), messenger bags, and purses.

- User memory and gesture reproducibility: The impact of user memory was tested by collecting samples a week after a user first performed a gesture. Users were first asked to perform the gesture without any video or text prompt. After a few samples were recorded, the user was shown a prompt and asked to perform the gesture again. These last samples measure reproducibility.
Of the 20 samples recorded for each gesture, each of the described scenarios has 5 samples recorded. The following table summarizes the degradation scenarios that were used for each gesture.
| Session ID | S gesture | User-defined gesture |
|---|---|---|
| Session I | 1. Observe video and text description of gesture 2. No degradation: Perform gesture normally (5 times) 3. Personal effects: Wear a coat or carry a bag. 4. Perform gesture with personal effect (5 times) |
1. Create a custom gesture 2. No degradation: Perform gesture normally (5 times) 3. Personal effects: Wear a coat or carry a bag. 4. Perform gesture with personal effect (5 times) |
| Session II ( a week after) | 1. Memory: Perform gesture from memory (5 times) 2. Observe video and text description of gesture 3. Reproducibility: Perform gesture (5 times) |
1. Memory: Perform gesture from memory (5 times) 2. Observe video of prior performance from session I 3. Reproducibility: Perform gesture (5 times) |
Downloads
Data is provided in the form of unprocessed skeletal joint coordinates. BLD-M provides 3 files (2 MATLAB .mat files and a .zip). Gesture sequences (unprocessed skeletal joint coordinates) are stored in the .mat files and can be accessed using specific indexing of the cell data structure. Each gesture has it’s own .mat file. We have also provided a .zip with helper functions that visualize the skeletal sequences, as well as a sample script that shows how to extract and display a gesture. Index definitions used in the sample script can be found in the next section: Data Labels and Definitions.
If used correctly, the function sample.m provided will extract two gesture samples from the data-set and display them. The following videos illustrate the output that it should yield.
Data Labels and Definitions
The following section contains information pertaining to the data-set (gesture types, index definitions, etc).
For the cell data structure data, we can access a specific gesture as follows:
data{subject_id,session_id,sample_id,view_id}
ID definitions are provided in the following tables.
User-defined Gesture Descriptions
| Subject ID | Description | Subject ID | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Double armed backstrokes | 21 | Shoot basketball |
| 2 | Y of Y-M-C-A | 22 | Parallel arms forward |
| 3 | Backwards jump-rope | 23 | Muscular pose |
| 4 | Backhand Tennis Swing | 24 | Wipe away motion |
| 5 | X-pose | 25 | Kamehameha |
| 6 | Upper body stretch | 26 | Upwards pose |
| 7 | Upper meditation | 27 | Salute |
| 8 | Halfway spin | 28 | Rockstar |
| 9 | Left arm chopping | 29 | Double clap |
| 10 | Long swimming frontcrawl | 30 | Stretches |
| 11 | Crouch forward swim | 31 | Taichi pose |
| 12 | Left-right body tilt | 32 | Taichi stretches |
| 13 | Arm-to-head stretch | 33 | Double wave |
| 14 | Balance-something | 34 | Stretch leg up |
| 15 | Chopping action | 35 | Jump pose |
| 16 | Dribble | 36 | Golf swing |
| 17 | Assorted poses | 37 | Shake imaginary maracas |
| 18 | Upper stretches | 38 | Y of Y-M-C-A (duplicate) |
| 19 | Upper flutter | 39 | Slow wave |
| 20 | Stretch and bend | 40 | Double hand stretch left right |
Gesture Type
| Session ID | Sample ID | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | [1 – 5] | No Degradations |
| 1 | [6 – 10] | Personal Effects |
| 2 | [1 – 5] | User Memory |
| 2 | [6 – 10] | Gesture Reproducibility |
Personal Effects Listing
For samples involving personal effects, users were assigned to either hold an object or wear clothing. The assignments are shown as follows.
| Personal Effect | Subject IDs with Effect |
|---|---|
| Holding Object | [1 – 7], 10, 15, 19, 22, 23, 25, [27 – 29], 34, 36, 38, 40 |
| Clothing | 8,9, [11 – 14], [16-18], 20, 21, 24, 26, [30-33], 35, 37, 39 |
View ID
| Kinect Viewpoint (View ID) | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Left |
| 2 | Right |
| 3 | Center |
| 4 | Back |
Missing Data
The following data is unavailable and will appear as an empty matrix in the cell array.
| Gesture | Subject ID | Session ID | Sample ID | View ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | 1 | 1 | 9 | 4 |
| User Defined | 10 | 2 | 10 | 4 |
| User Defined | 18 | 2 | 10 | [3 – 4] |
| User Defined | 37 | 1 | [7 – 10] | * |
Off-labeled Data
The following data is available for use in the data-set, but conflicts with prior labels.
| Gesture | Subject ID | Session ID | Sample ID | View ID | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | 25 | 1 | [6 – 10] | * | No Personal Effects |
| S | 38 | 1 | [6 – 10] | * | No Personal Effects |
Citations
If you use this dataset (BLD-M), please kindly cite the following paper:
- J. Wu, J. Konrad, and P. Ishwar, “The Value of Multiple Viewpoints in Gesture-Based User Authentication,” in the Proc. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Workshop on Biometrics, Columbus, OH, 23 Jun., 2014.
Acknowledgements
This dataset was acquired within a project supported by the National Science Foundation under CNS-1228869 grant.
We would like to thank the students of Boston University for their participation in our dataset. We would also like to thank Luke Sorenson and Lucas Liang for their significant contribution to the data gathering and tabulation processes.
F.A.Q.
Q: Why is there only skeletal data and no RGB and depth map data?
A: At this time, we are only able to share skeletal data.
Contact
Please contact [jonwu] at [bu] dot [edu] if you have any questions.